As a web server, the reverse-proxy lets you define multiple web site rules.
All the servers specified in the rules operate as separate virtual web servers.
As a result, you need to adopt an approach that allows you to determine which server will handle specific incoming requests.
The default server is the first saved in the table, unless you include the default server option in the site rule to explicitly designate a default server.
It's a good idea not to use this option, as it means that there are web requests that are not being processed as they should be.
If you want to avoid and prohibit requests outside the scope of your rules, it's best to use the site rule as follows.
Let's say you want to define a kind of catch-all for domains for which your reverse-proxy does not have the associated rules.
Note that you can only specify one default site rule. There is no sense in having several default sites.
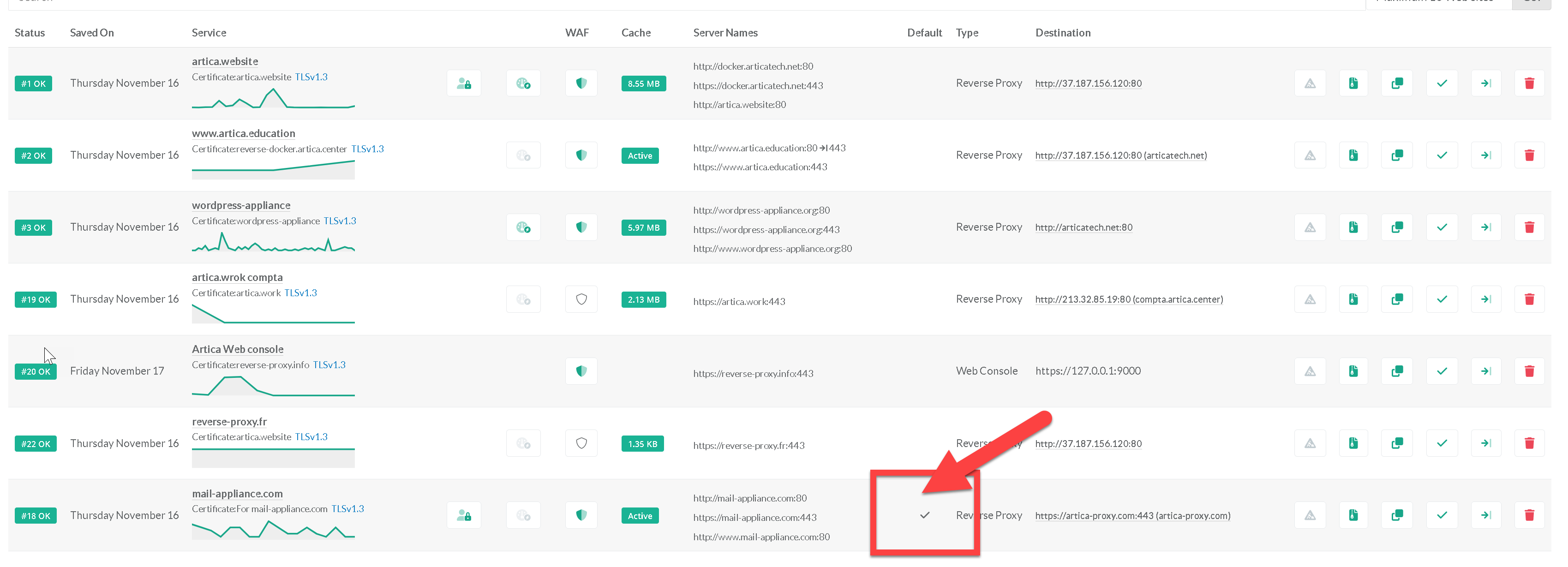
- On the web service main table, select the web service you want to define as default server
- Clock on the service name row to open general parameters of the service
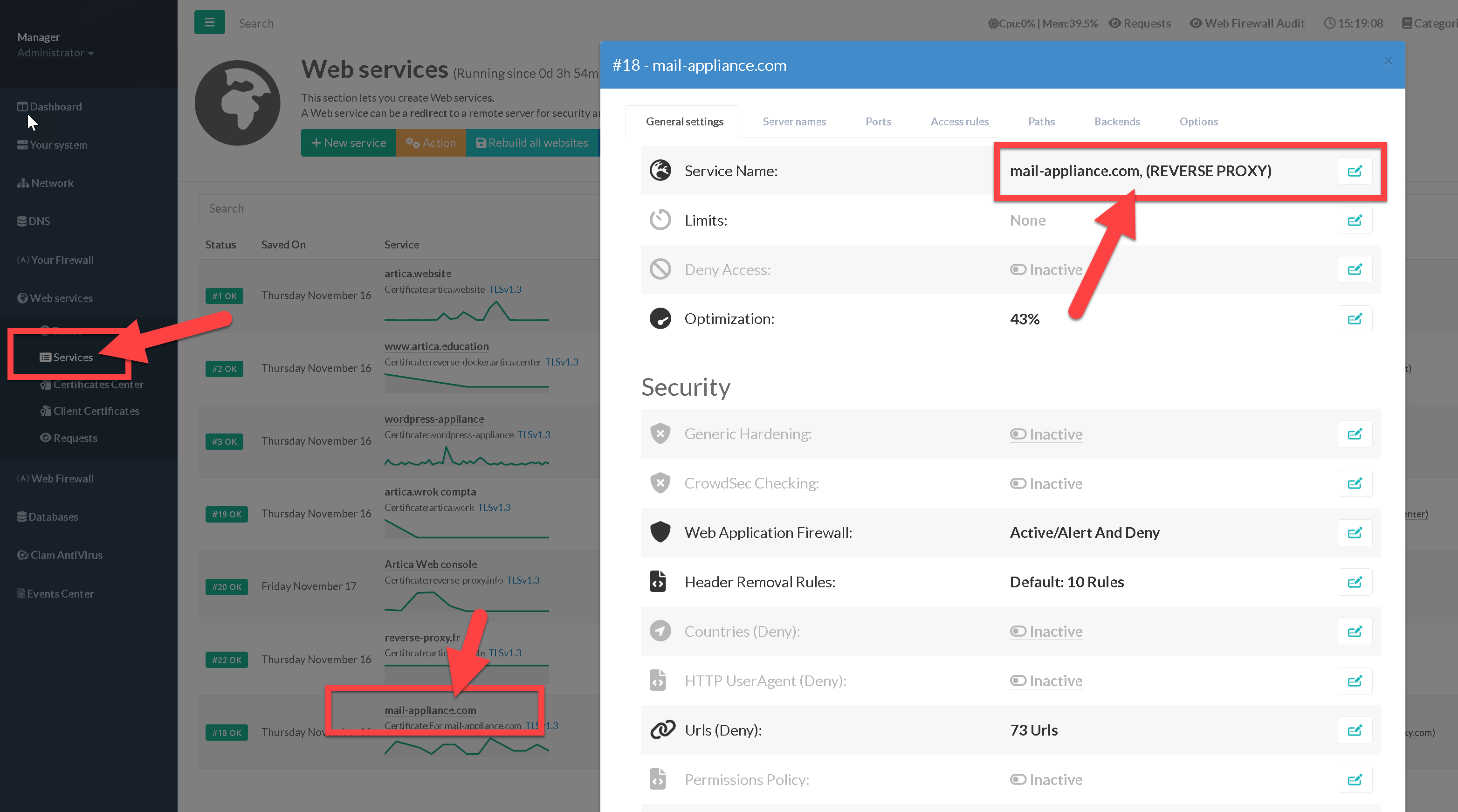
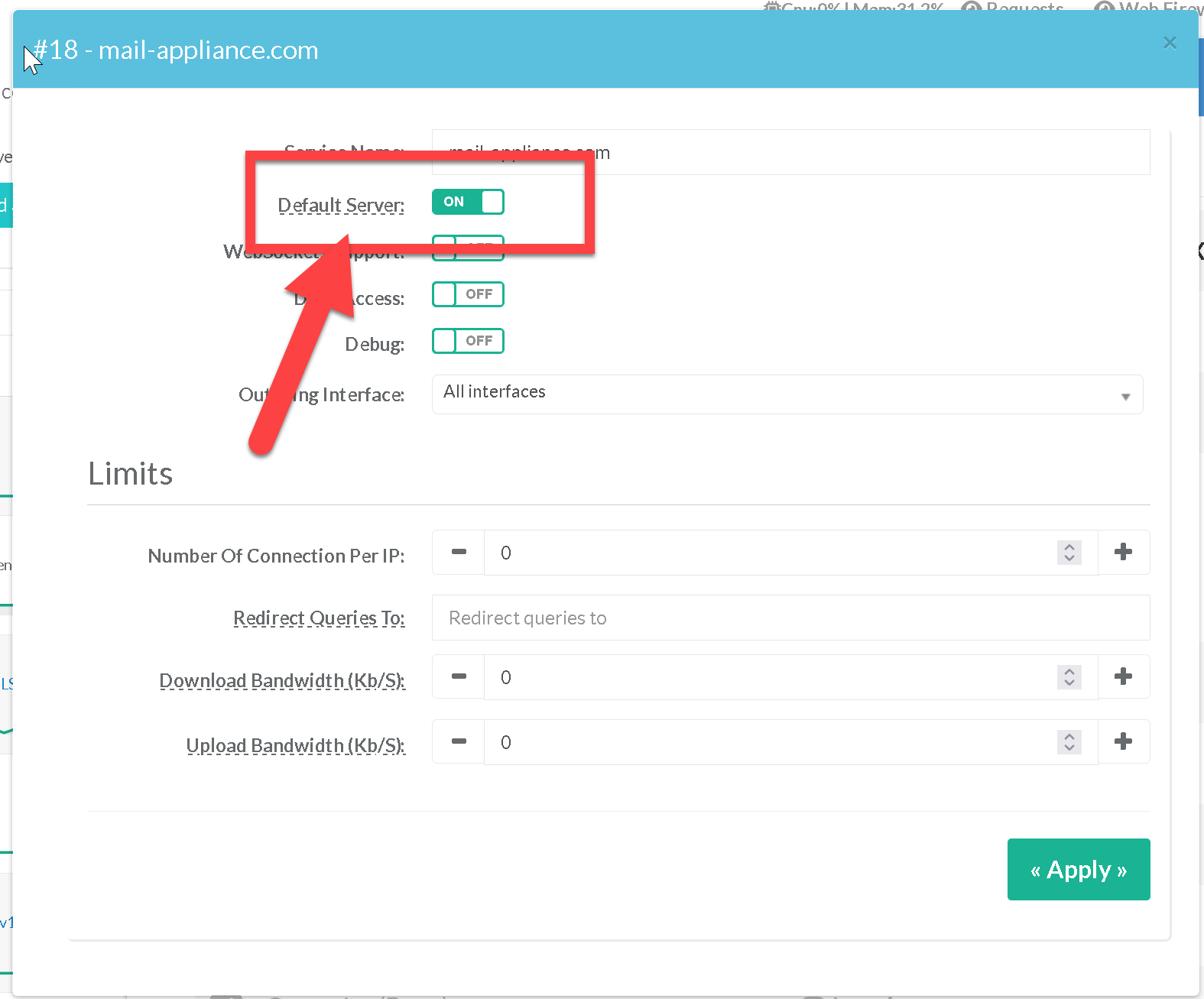
- Click on the checkbox “Default server”
- Click on Apply Button
- A new check mark will be displayed in the default server column of your server rule.