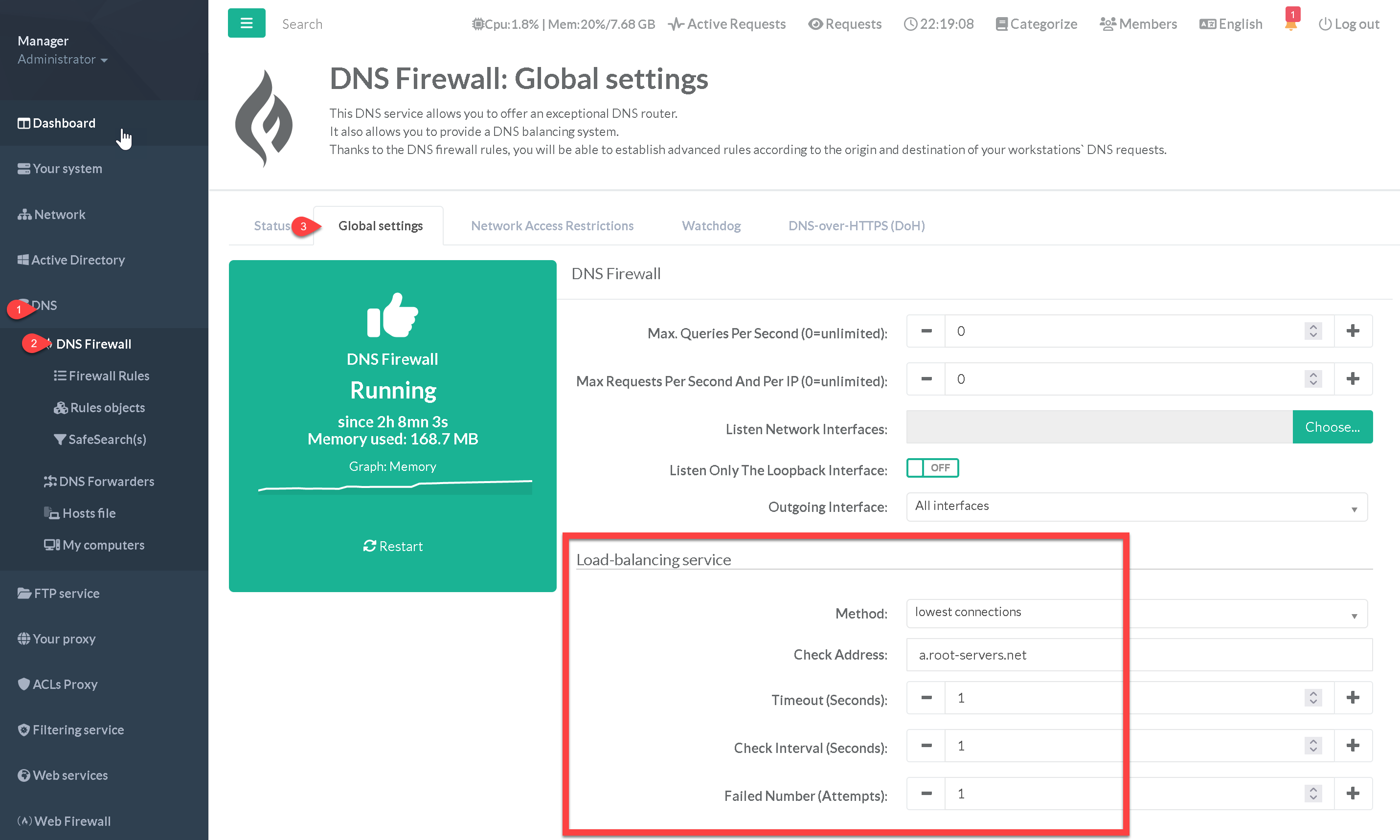
The DNS Firewall uses health-check queries, sent once every second, to determine the availability of a backend server.
This feature as been improved in Artica v4.30 Service Pack 969
¶ Least outstanding
The load balancing policy is called least outstanding, which means the server with the least queries ‘in the air’ is picked.
The exact selection algorithm is:
- Pick the server with the least queries ‘in the air’ ;
- In case of a tie, pick the one with the lowest configured ‘order’ ;
- in case of a tie, pick the one with the lowest measured latency (over an average on the last 128 queries answered by that server).
¶ The health-check
By default, an A query for the “a.root-servers.net” name is sent.
If the health-check is failed the backend DNS server The is considered as down
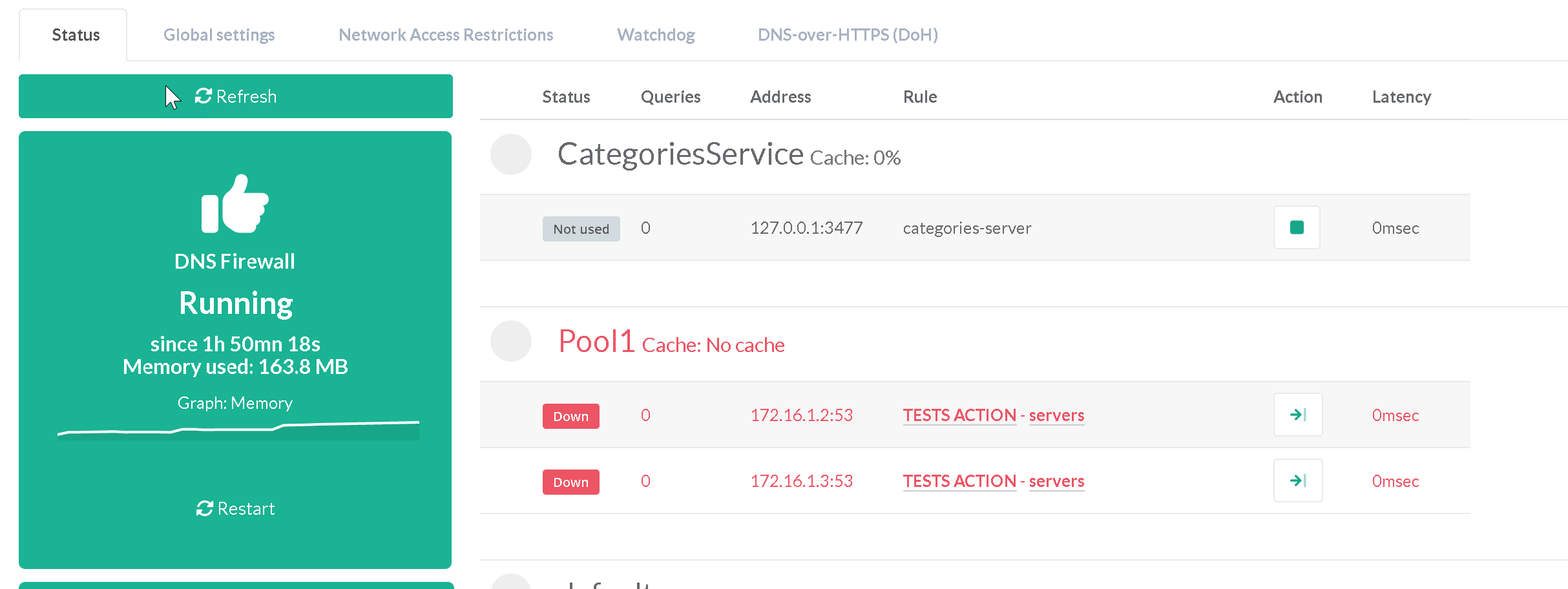
In some cases, you may be able to use the DNS firewall to a DNS server that does not have the ability to resolve a.root-servers.net.
If this is the case, you should change the hostname to be resolved so as not to influence the DNS firewall towards inappropriate behavior
¶ Set the health-check parameter inside a rule
- Inside a Firewall rule, a dedicated section “Load-balancing service” defines the healthcheck parameters.
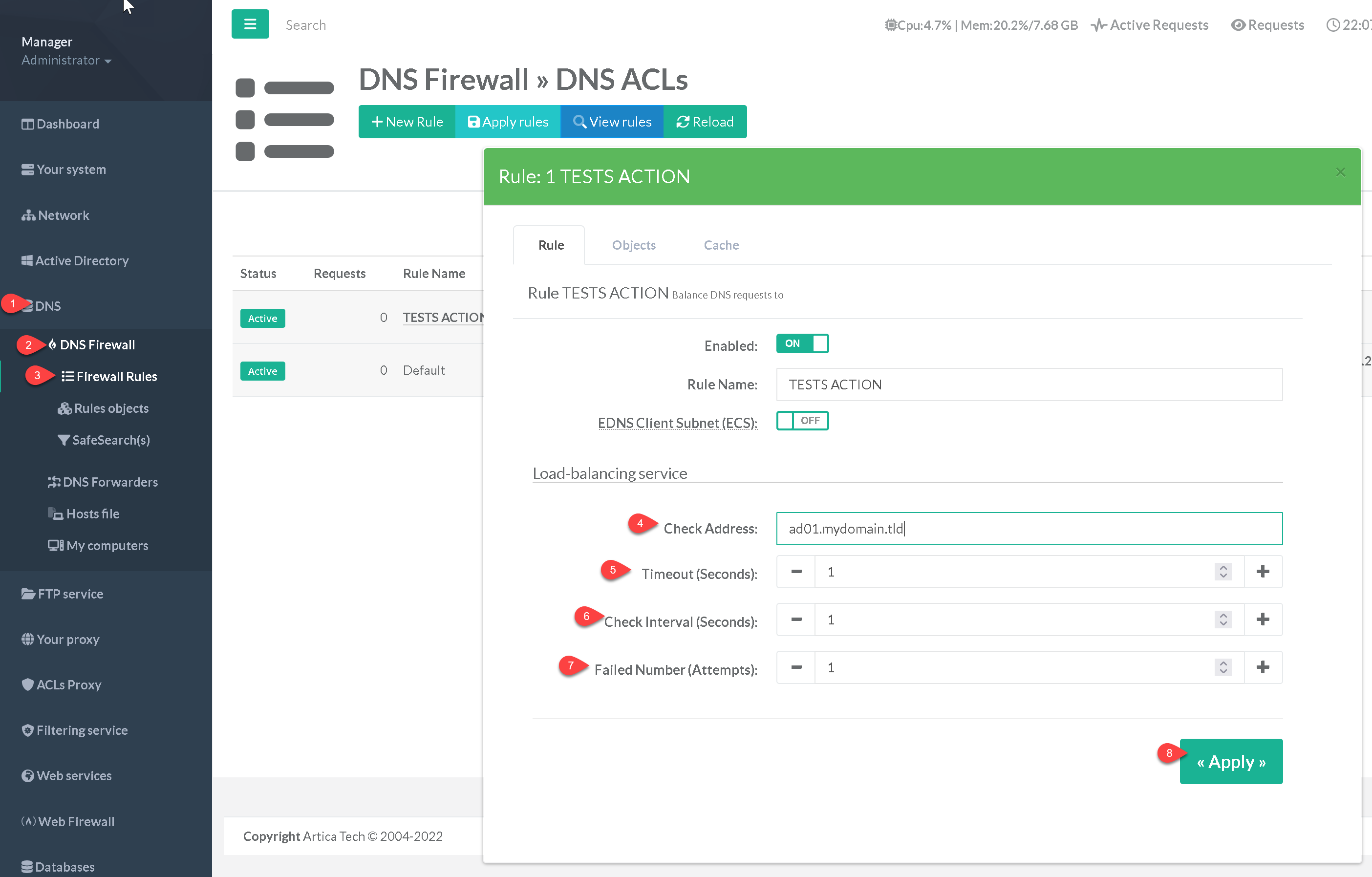
- The Check Address Is the host name that will be resolved during the test phase.
Make sure that this address is properly resolved by the destination DNS server. - The interval between two health-check queries can be set via the Check Interval parameter, and the amount of time for a response to be received via the Timeout one.
- The number of health check failures before a server is considered down is configurable via the Failed Number parameter, defaulting to 1.
¶ Set the health-check parameter for default servers.
The standard DNS servers you specify in the system are transformed into a load-balancing farm and have the same options.
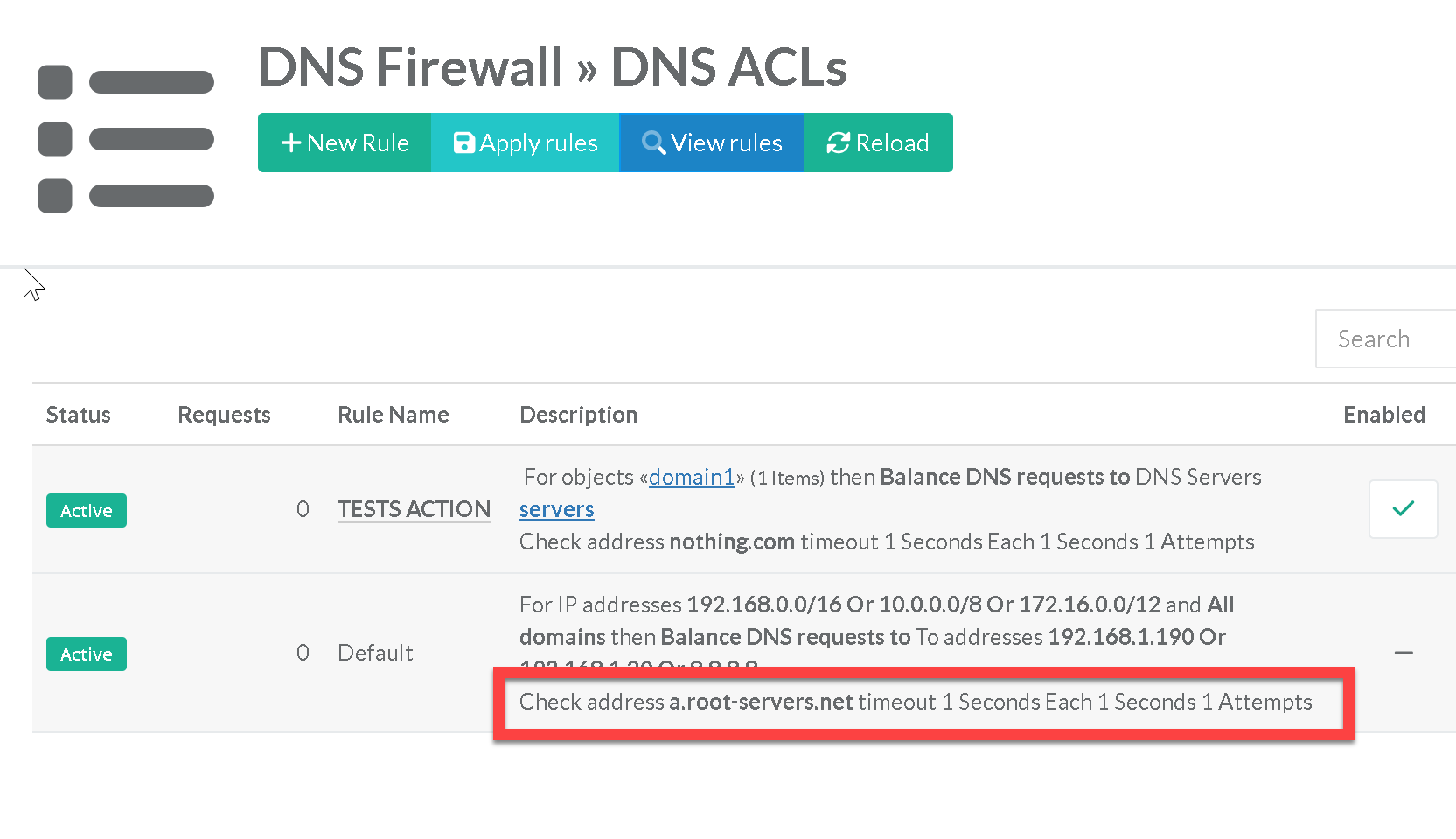
- Same options are available in “
DNS” > “DNS Firewall” > “Global settings”