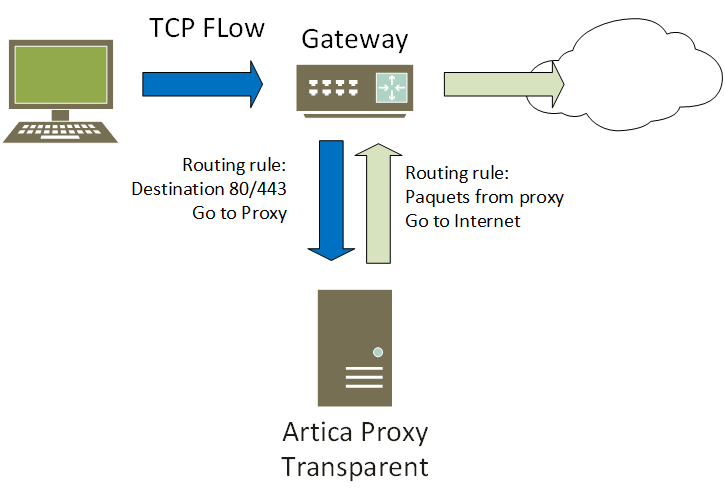
The transparent mode is designed to intercept web flows and pass them through the local proxy service
The proxy in transparent mode does not need the browser's consent to be introduced into the organization.
There are a number of methods for diverting HTTP flows to the proxy ( WCCP, MikroTik ).
The simplest method is to make the proxy the Internet gateway.
¶ How it works ?
In other words, to make the transparent mode work, you need to have your internal gateway send the flows back to the proxy, or simply have your workstations use the proxy as a gateway.

¶ Intercept Mode (Transparent Interception) benefits
- Ease of Deployment:
Intercept mode is often easier to set up and requires minimal changes to the existing network infrastructure.
It's typically a matter of configuring NAT rules on a router or firewall to redirect traffic to the proxy server. - Broad Compatibility:
This method is widely supported across many network devices and does not have special requirements on the proxy server’s operating system. - Simplicity:
For HTTP/HTTPS traffic, interception mode provides a straightforward way to enforce content filtering, caching, or security policies without needing to manage IP routing.
¶ Limits of the transparent interception:
- Source IP Address Modification:
Intercept mode usually changes the source IP address to that of the proxy server, making it difficult to identify the original client behind the proxy.
This can be a significant drawback for logging, compliance, and troubleshooting. - Limited by Protocol:
Primarily effective with HTTP/HTTPS traffic.
While possible with other TCP-based services, it might not be as straightforward or effective. - Potential for Encrypted Traffic Issues:
Intercepting SSL/TLS traffic requires the proxy to terminate and then re-establish the encrypted connection, which can lead to issues with certificate validation unless properly handled.
¶ Create an HTTP transparent proxy port (Port 80)
Artica's transparent ports meet this need.
The easiest way is to create two ports that will focus on destination ports 80 and 443
- On the left menu, choose “
Your Proxy” > “Listen ports” - Choose the
Transparent portstab - Click on
New port
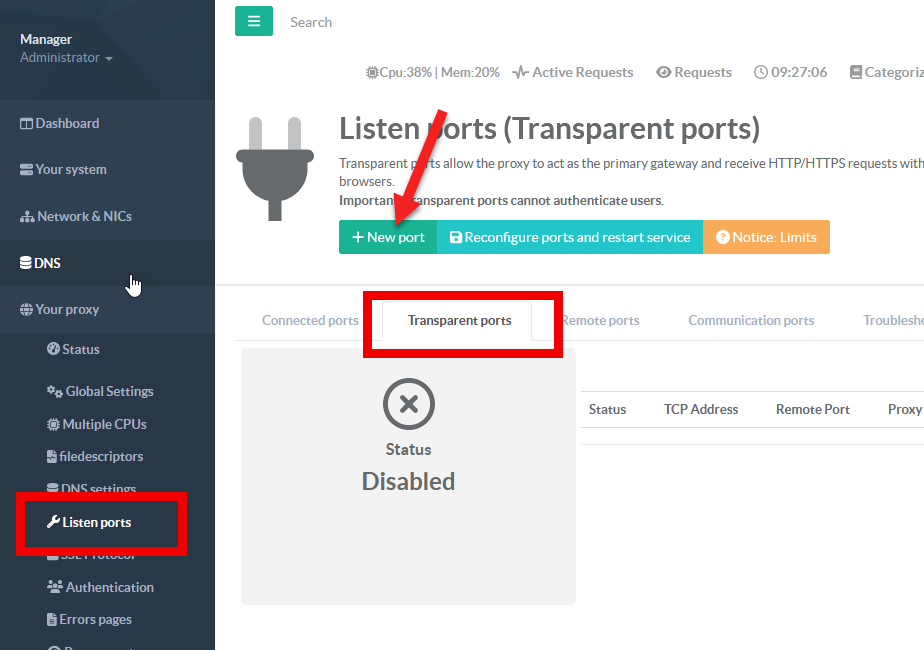
- On the destination port, set the 80 port

- The proxy port field is optional;
Artica offers you a randomly generated one because it is used locally.
The field is present to prevent local port conflicts. - If you have several network cards and want to force the proxy to use a specific network card to exit to the Internet, enter the network card in the "Forward Interface" field.
¶ Create an HTTPs transparent proxy port (Port 443)
- Click again on
New port - On the destination port, set the 443 port

- In "Use a certificate from certificate center", select a certificate.
Don't worry about the certificate: it's used internally, as the default proxy doesn't decrypt the SSL protocol.
It just needs a certificate to work.
If you really want to decrypt/encrypt through the proxy, the certificate used by the proxy must be installed in your users' browsers.
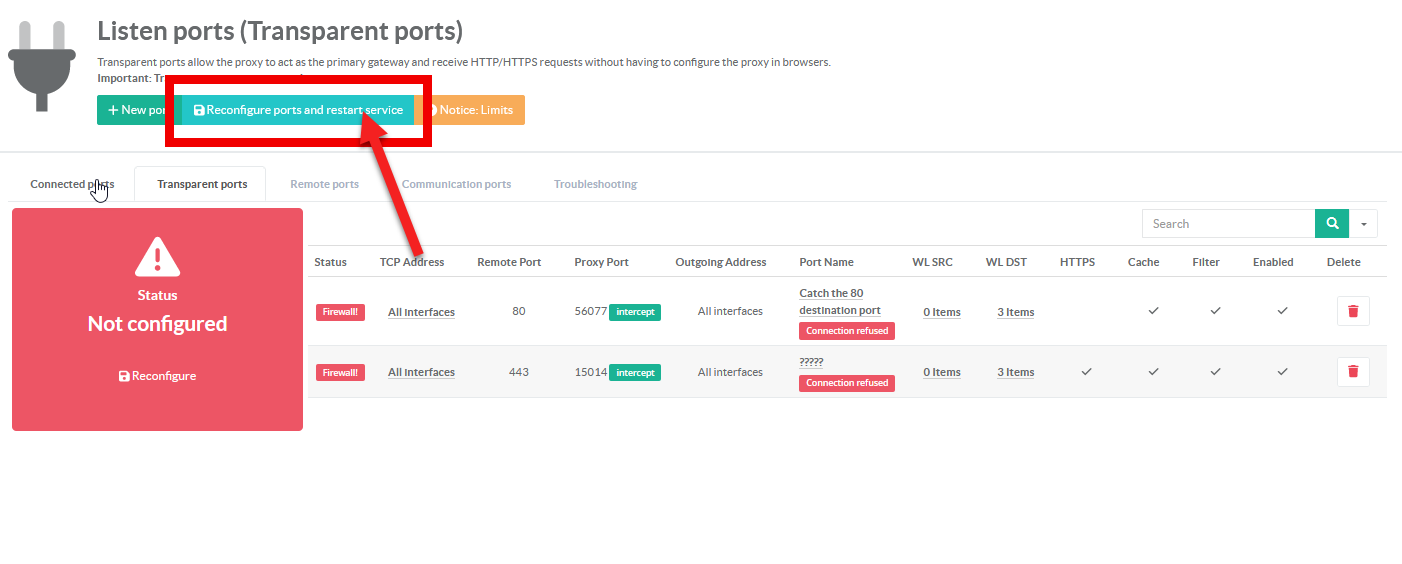
¶ Finally, compile your configuration.
After adding your ports, Artica performs an audit of your configuration.
As the parameters have not been applied, your settings are not in line with the system.
- Click on the "Reconfigure an restart service" button to put your settings into production mode.
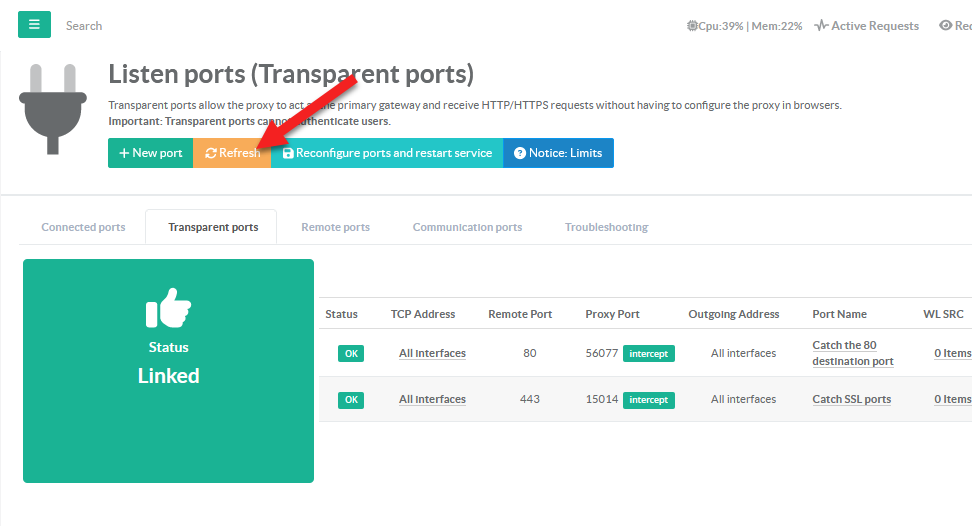
¶ Network checks
- Make sure all states are green.
- Click on
Requestson the top menu. - You should see requests from your workstations
