Virtual Local Area Networks are used to divide a physical network into several broadcast domains.
To be able to make use of VLANs you will need a switch (or several) that support the IEEE 802.1q standard.You will also need a NIC (Network Interface Card) that plays nice when used to transmit and receive tagged packets.
Many NICs do support 802.1q but some have trouble with the extra 4 bytes added to the packet when tagged packets are used.The reason to use VLANs is to divide a network and separate hosts that shouldn't be able to access each other. Artica VLAN feature address the IEEE 802.1q standard way of doing this division.
There are two types of packets on a VLAN, these are tagged and untagged packets.
- The tagged packet is a regular packet and looks just like a packet that exists on a regular network.
- Untagged packets are the most common type on a VLAN.
The decision of which VLAN an untagged packet belongs to is made by the switch.
A switch can be configured to assign specific ports to specific VLANs.
The switch can also be configured to receive tagged packets.
If the switch receives a tagged packet and the port which it receives the packet with is configured to allow tagged packets, it knows which ports it can send the packet to.
A switch can also be configured to transmit tagged packets, this could be used to make a VLAN span more than one switch or to make use of a VLAN aware NIC (Network Interface Card) on a router, firewall, server or even a workstation.
A VLAN is assigned a specific id.
This id can be anything between 1 and 4094.
VLAN 1 is most commonly used for management so this should not be used.
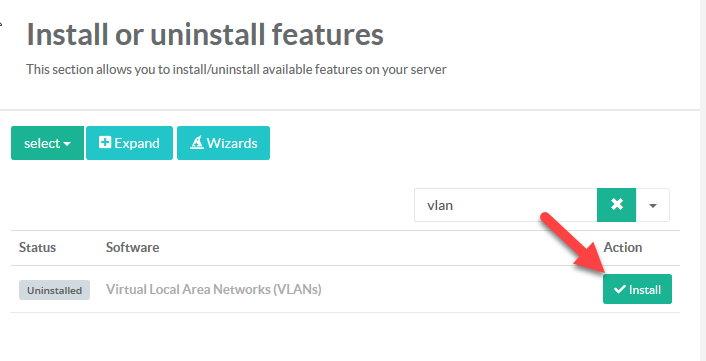
¶ Install the VLAN Feature
- On the left menu, choose
Your system >Features - On the search field, type “
vlan” - Click on install button under “Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs)"
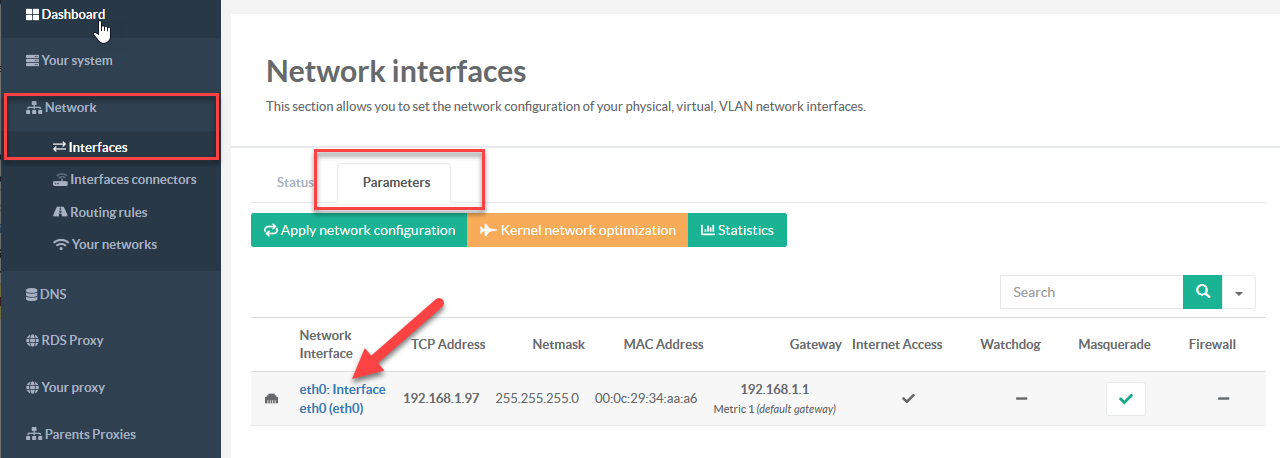
¶ Create a VLAN Inteface
- On the left menu, choose “Network” and “Interfaces”
- Select “Parameters” tab.
- On the main table, choose your main interface that will handle the VLAN interface.
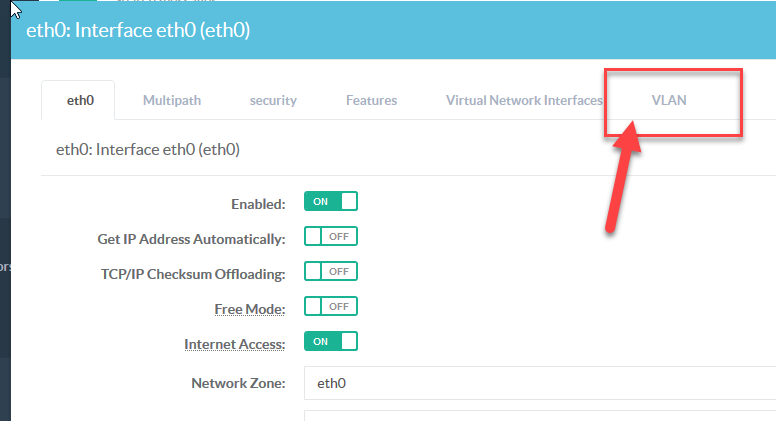
- Select "VLAN" tab
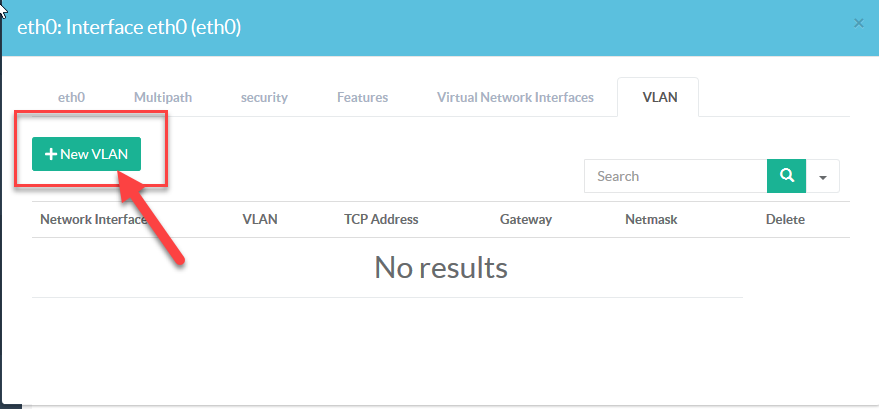
- Click on the “New VLAN” button.
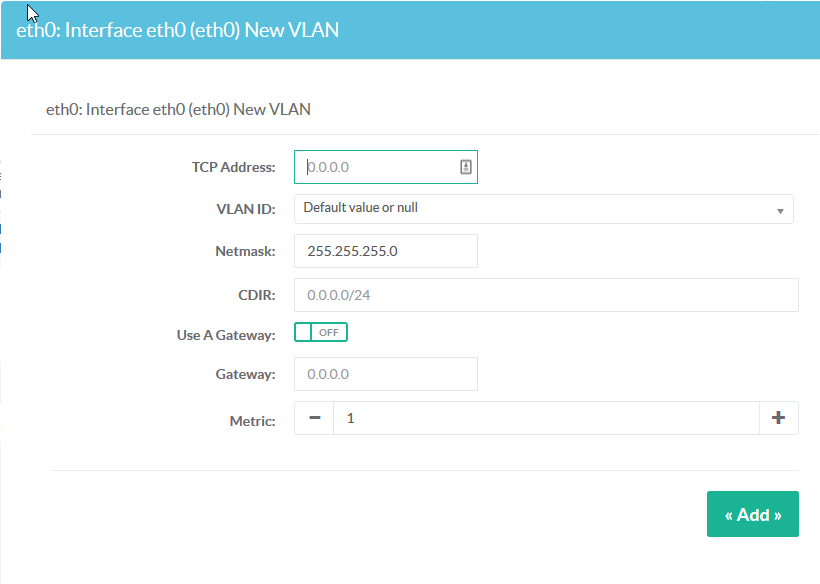
- Define the TCP address of the VLAN interface
- Choose the VLAN ID
- Set the netmask
- Set the CDIR format.
- If you want to force the VLAN interface to use a specific gateway, turn on the “Use a Gateway” and set the gateway and the metric value to define the VLAN interface order.
The Interface is directly compiled after adding or modify it, you did not have to compile the whole network to make the Network interface active.