NIC bonding or link aggregation is a method allows multiple physical interfaces to be aggregated into a single link, balancing traffic and providing failover capabilities based on the selected mode, such as round-robin or active-backup.
This feature is available since Artica v4.40 or Artica v4.30 with Instable Service Pack version 719
LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) is a standardized method (defined in IEEE 802.3ad) for combining multiple network interfaces into a single logical interface to increase bandwidth, redundancy, and fault tolerance.
It dynamically negotiates and manages the aggregation of links with a compatible switch.
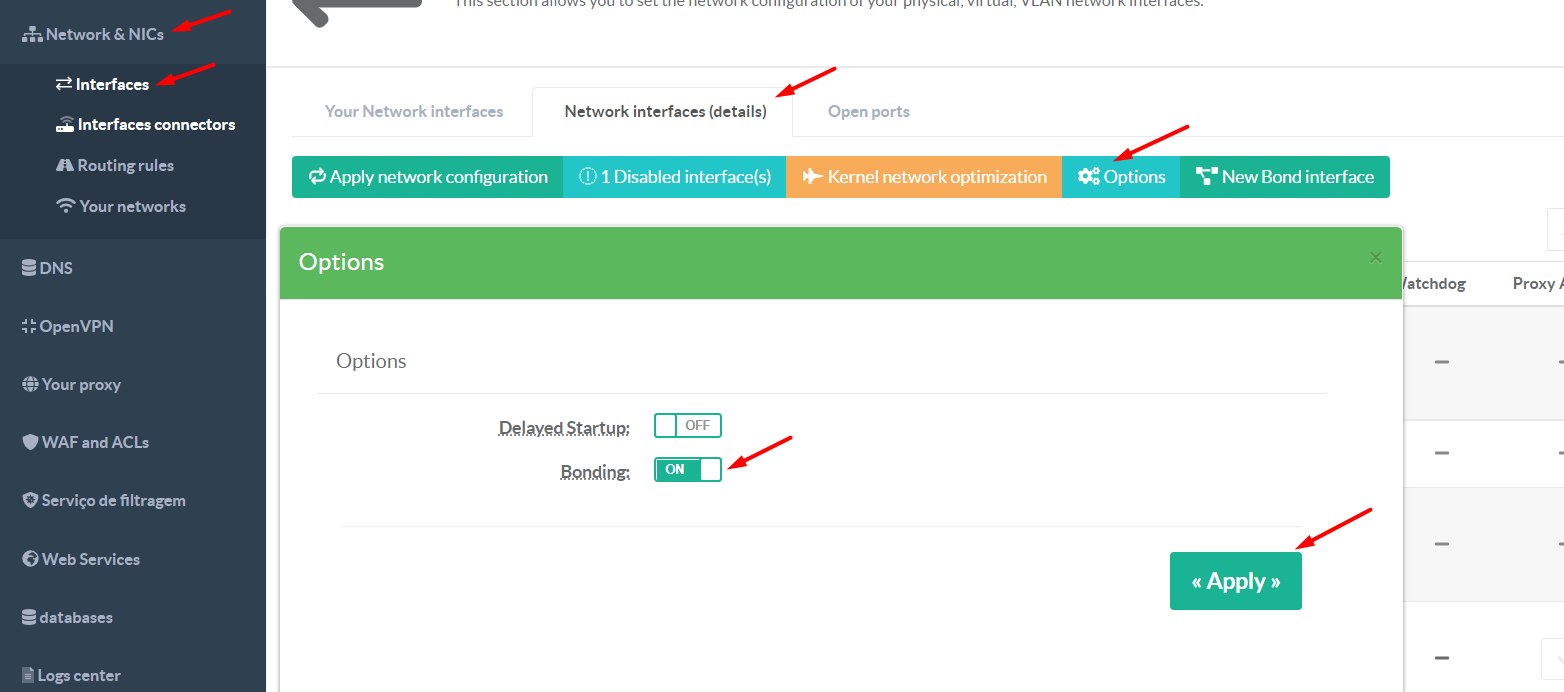
¶ Enable the Bonding feature
- On left go to
Network & Nics > Interfaces - Click on Network interfaces (details) tab
- Click on the Options button
- Turn on the Bonding feature
Click on Apply button
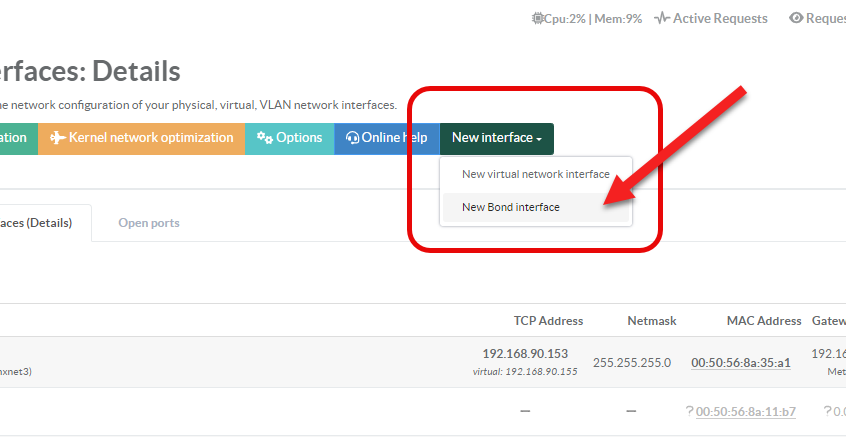
¶ Create a Bond Interface
- Click on the New Interface button an select New Bond Interface
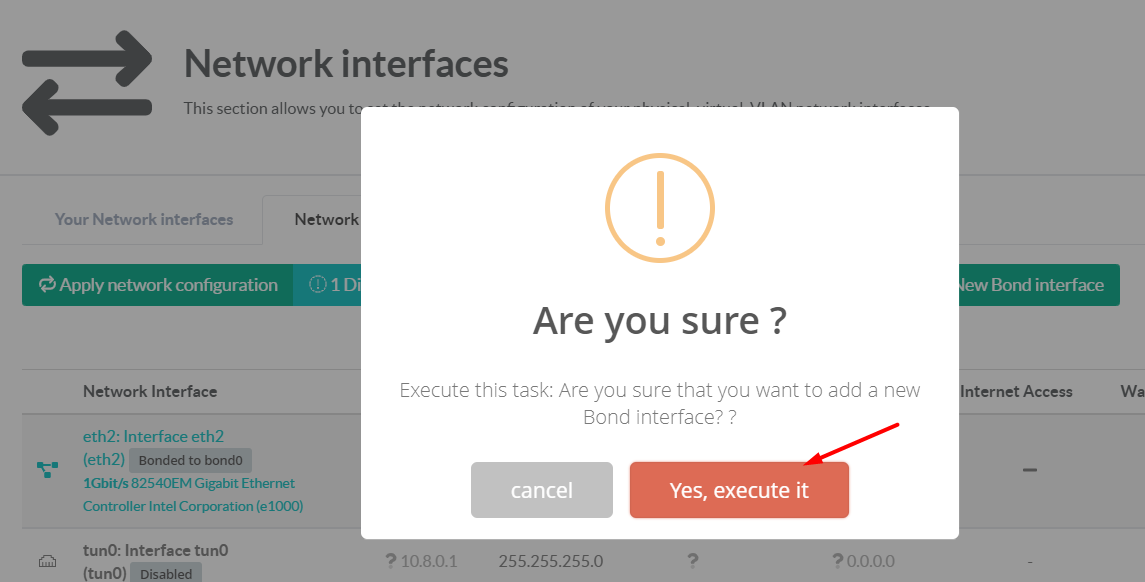
- Click Yes on confirmation popup.
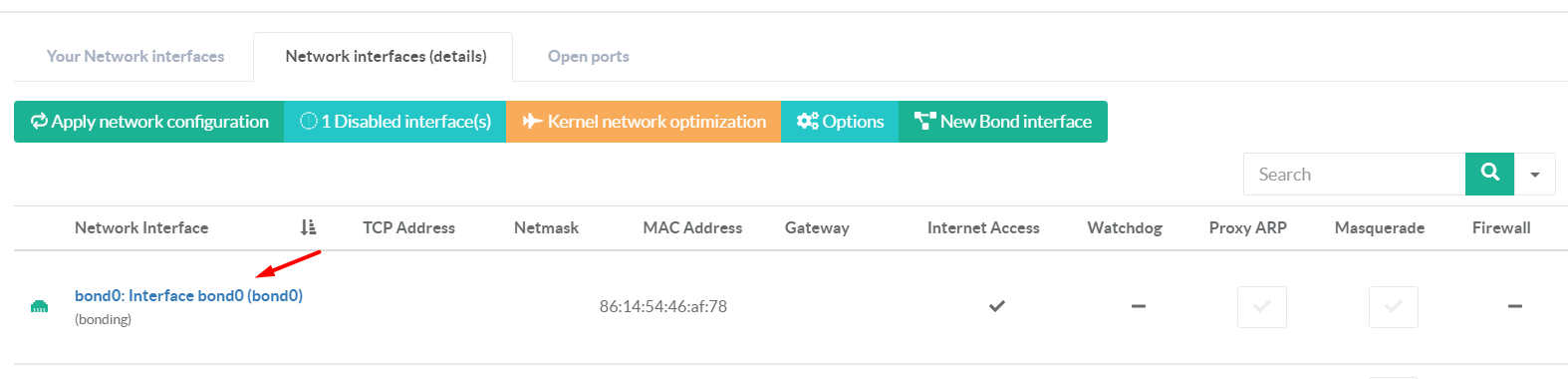
¶ Setup Bond main Interface
- Click on the bond interface you want to configure on the main table.
- Set the network information for this interface (ip, netmask, gateway,...) like a standard network interface.
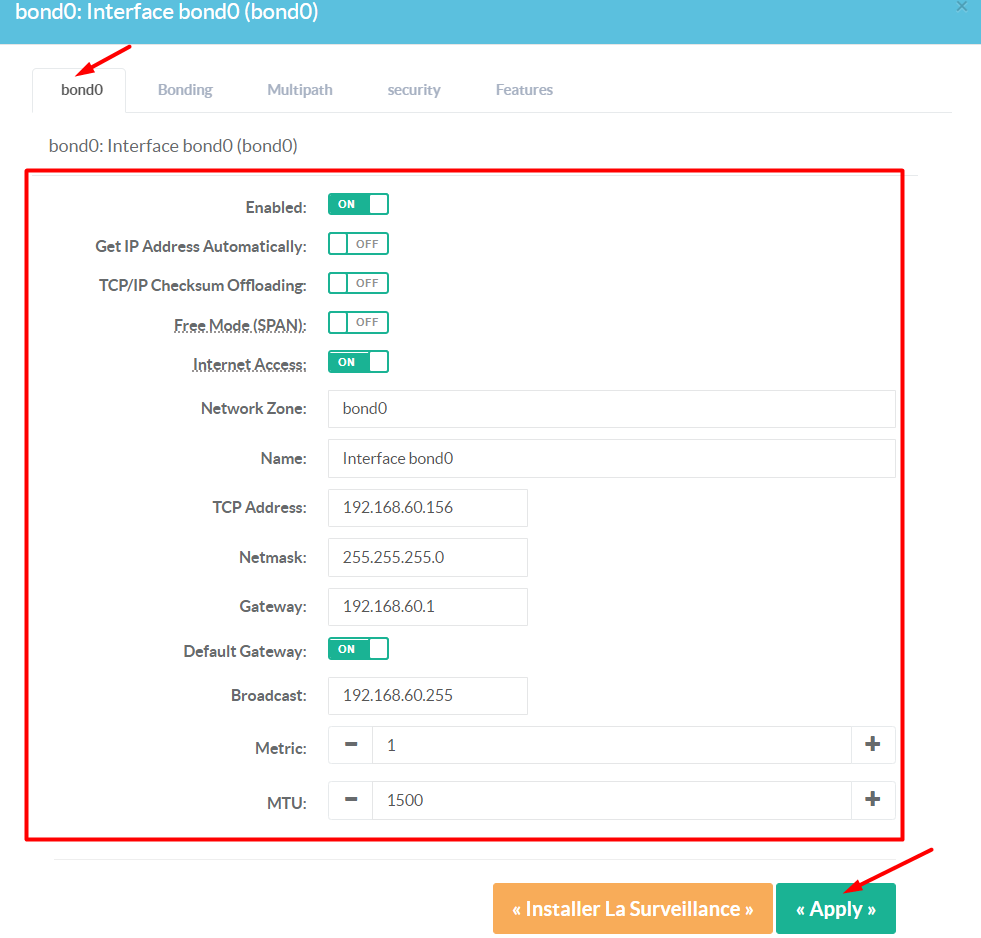
Click on Apply button
¶ Link physical interfaces to the Bond interface
- Select the Bonding tab
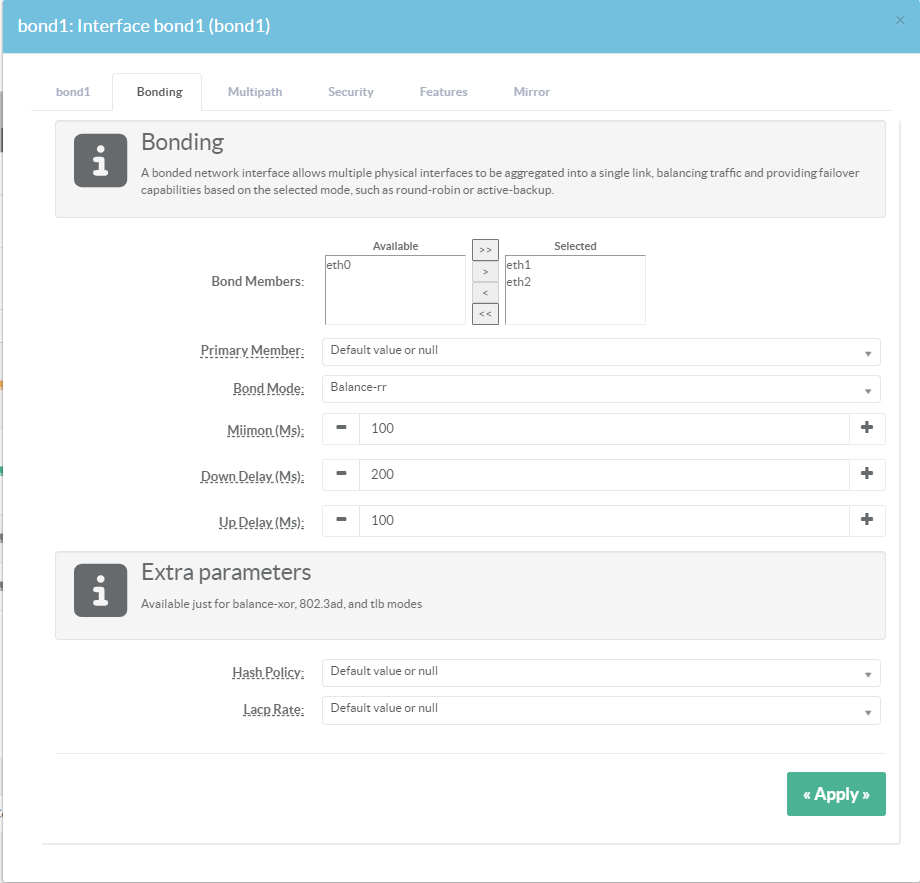
- Bond Members:
Specifies the network interfaces that will be linked to the bond primary interface.
- Primary Member:
Specifying which slave is the primary device.
The specified device will always be the active slave while it is available.
Only when the primary is off-line will alternate devices be used.
This is useful when one slave is preferred over another, e.g., when one slave has higher throughput than another.
This option is only valid for active-backup(1),balance-tlb (5) and balance-alb (6) mode. - Bond Mode :
Specifies one of the bonding policies / modes ( see Bond modes section )
- Miimon:
Specifies the MII link monitoring frequency in milliseconds.
This determines how often the link state of each slave is inspected for link failures.
A value of zero disables MII link monitoring.
A value of 100 is a good starting point.
The use_carrier option, below, affects how the link state is determined.
See the High Availability section for additional information.
- Down delay:
Specifies the time, in milliseconds, to wait before disabling a slave after a link failure has been detected.
This option is only valid for the miimon link monitor.
The downdelay value should be a multiple of the miimon value; if not, it will be rounded down to the nearest multiple.
- Up delay: Specifies the time, in milliseconds, to wait before enabling a slave after a link recovery has been detected.
This option is only valid for the miimon link monitor.
The up delay value should be a multiple of the miimon value; if not, it will be rounded down to the nearest multiple.
- Hash Policy
Selects the transmit hash policy to use for slave selection in balance-xor, 802.3ad, and tlb modes,
more info here https://docs.kernel.org/networking/bonding.html?highlight=xmit_hash_policy
- Lacp Rate - Option specifying the rate in which we'll ask our link partner to transmit LACPDU packets in 802.3ad mode.
more info here https://docs.kernel.org/networking/bonding.html?highlight=lacp_rate - Click Apply
- Click on the button Apply network configuration
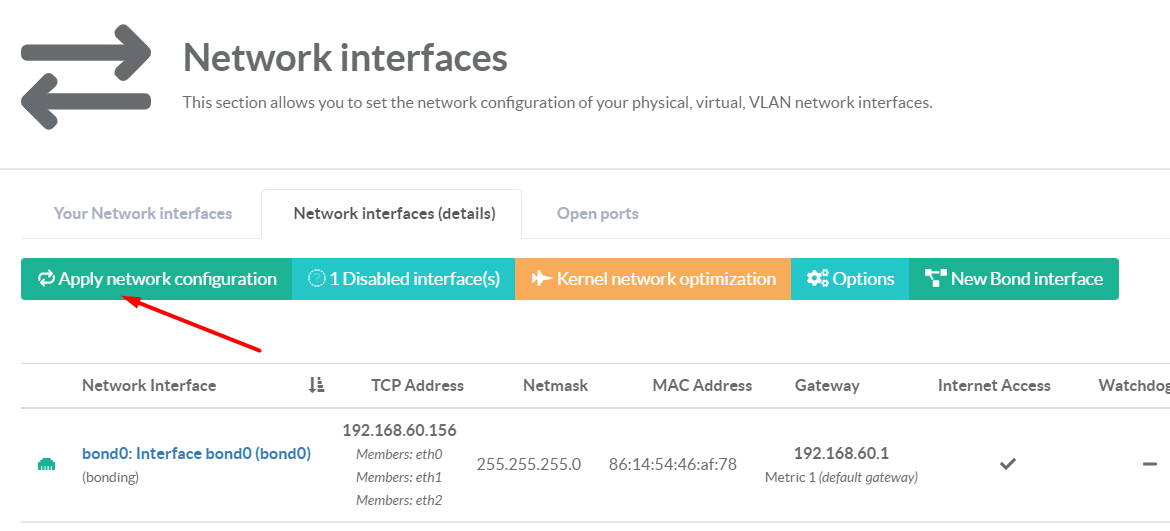
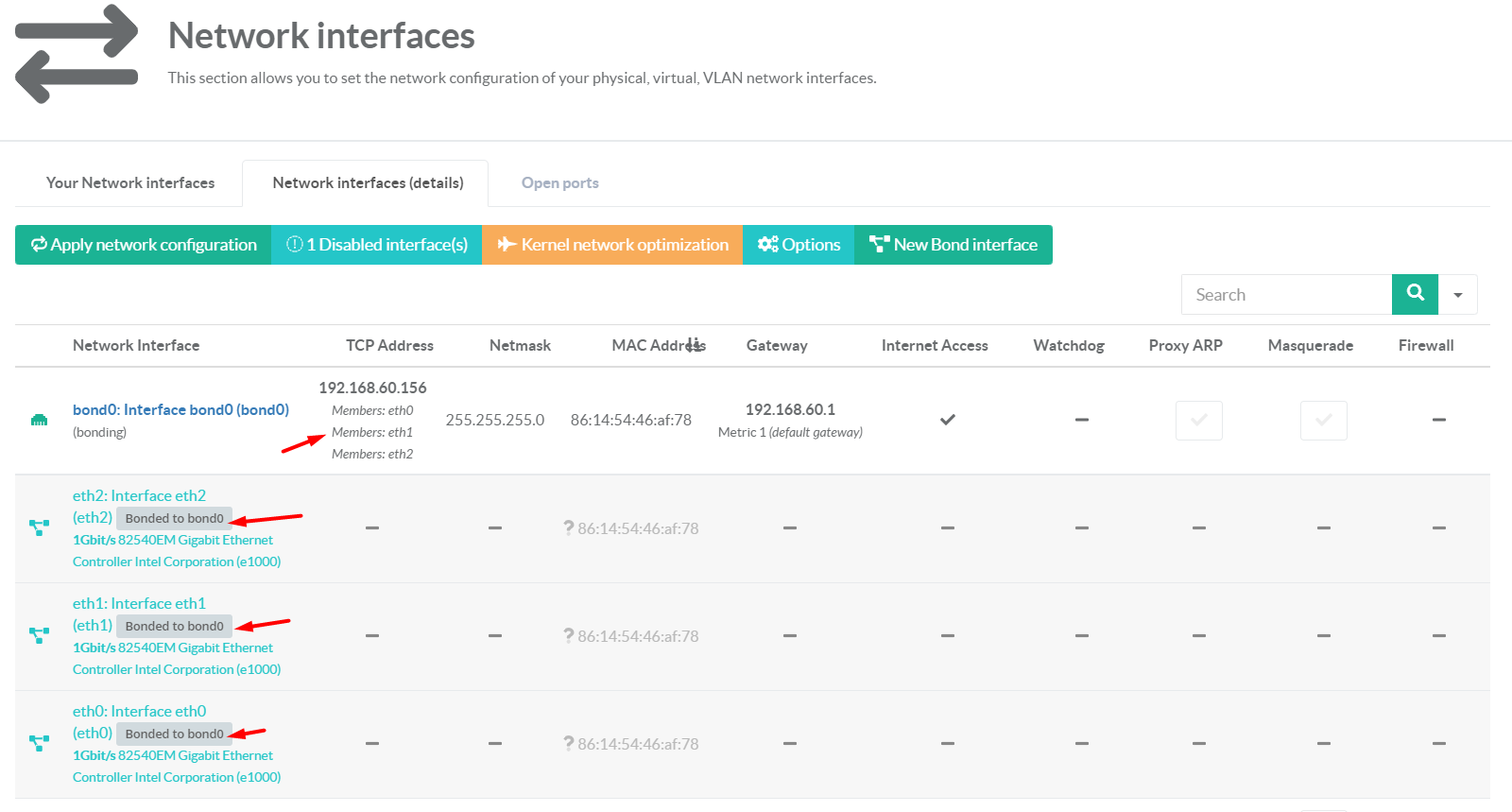
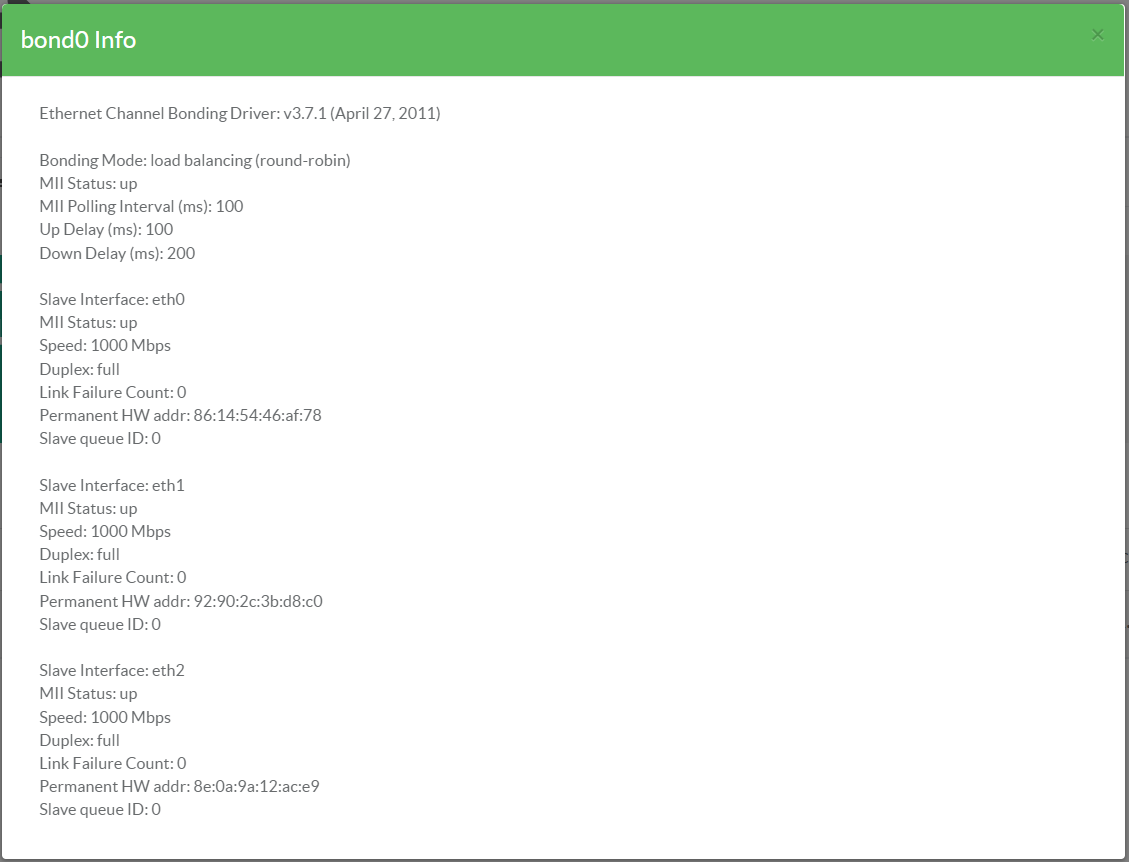
¶ Interface Status
To check the status of the bond interface:
- Click on the Your Network Interfaces tab
- Click on the magnified icon of the bond interface.
¶ Bond Modes
| Mode | Policy | How it works | Fault Tolerance | Load balancing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Round Robin | Packets are sequentially transmitted/received through each interfaces one by one. | No | Yes |
| 1 | Active Backup | One NIC active while another NIC is asleep. If the active NIC goes down, another NIC becomes active. only supported in x86 environments. | Yes | No |
| 2 | XOR [exclusive OR] | In this mode the, the MAC address of the slave NIC is matched up against the incoming request’s MAC and once this connection is established same NIC is used to transmit/receive for the destination MAC. | Yes | Yes |
| 3 | Broadcast | All transmissions are sent on all slaves | Yes | No |
| 4 | Dynamic Link Aggregation | Aggregated NICs act as one NIC which results in a higher throughput, but also provides failover in the case that a NIC fails. Dynamic Link Aggregation requires a switch that supports IEEE 802.3ad. | Yes | Yes |
| 5 | Transmit Load Balancing (TLB) |
The outgoing traffic is distributed depending on the current load on each slave interface. Incoming traffic is received by the current slave. If the receiving slave fails, another slave takes over the MAC address of the failed slave. |
Yes | Yes |
| 6 | Adaptive Load Balancing (ALB) |
Unlike Dynamic Link Aggregation, Adaptive Load Balancing does not require any particular switch configuration. Adaptive Load Balancing is only supported in x86 environments. The receiving packets are load balanced through ARP negotiation. |
Yes | Yes |