Destination NAT (DNAT) is a technique used in network address translation to change the destination address of packets as they pass through a router or firewall. DNAT is typically used to redirect incoming traffic destined for one IP address to another IP address, often within a private network. This is commonly used for scenarios like port forwarding, where traffic intended for a specific public IP and port is redirected to a private IP and port.
There are two steps to creating a NAT rule.
The first is to specify the type of rule and its destination.
This first rule will simulate a "network card" that you can use in the firewall rules in the second step.
¶ A) Create the main NAT rule.
- On the left menu, go to “
Your Firewall” > “NAT” - Click on
New Rulebutton
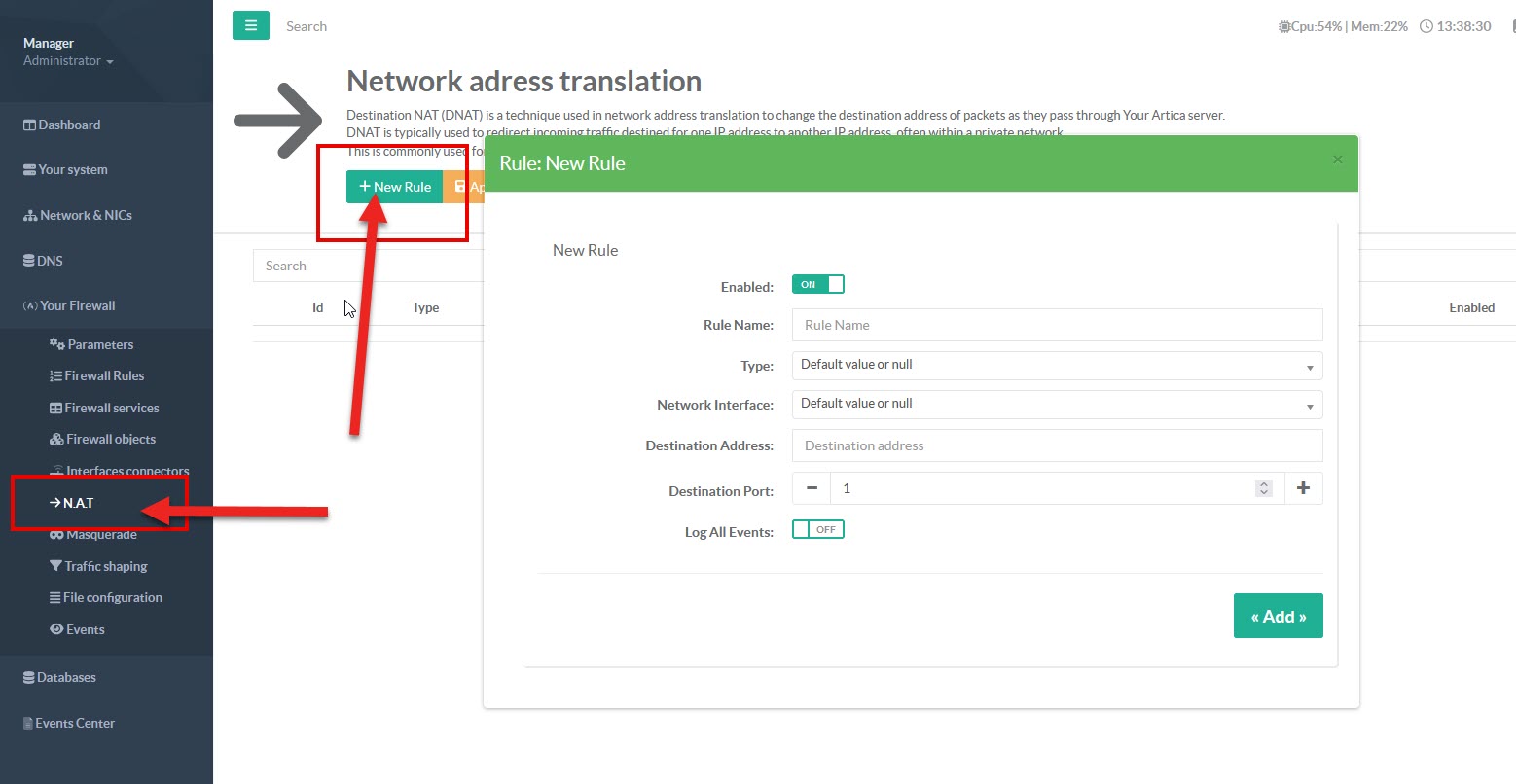
- Set the NAT rule name in “
Rule Name”' - Set the NAT type : Destination NAT (DNAT) or Source NAT
- Set the network card that will receive the connection request in “
Network Interface” - Enter the address of the target machine for this rule inside “
Destination Address” field - Set the destination Port
- If you turn on “
Log All events”, Network packets using this rule will be logged in the firewall's event log.
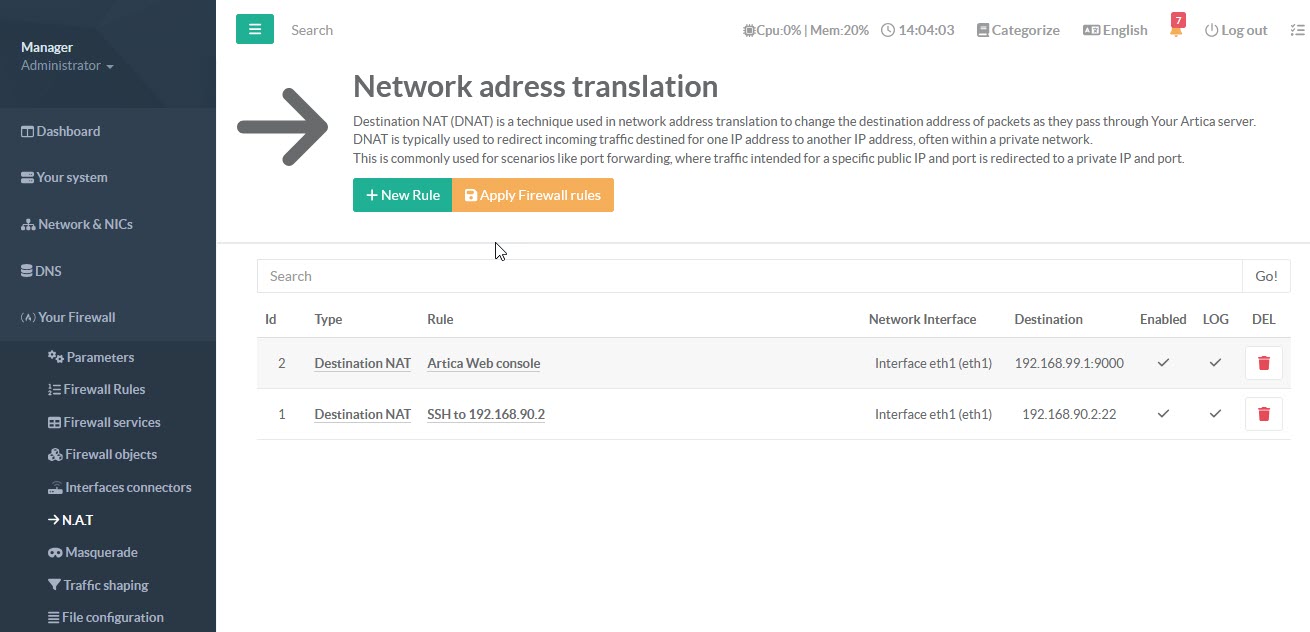
Our NAT rules have been added and, as you can see, there is no indicated incoming port here.
In fact, to set up this NAT rule, we need to go on to the next step
¶ Use the NAT rule inside a Firewall rule
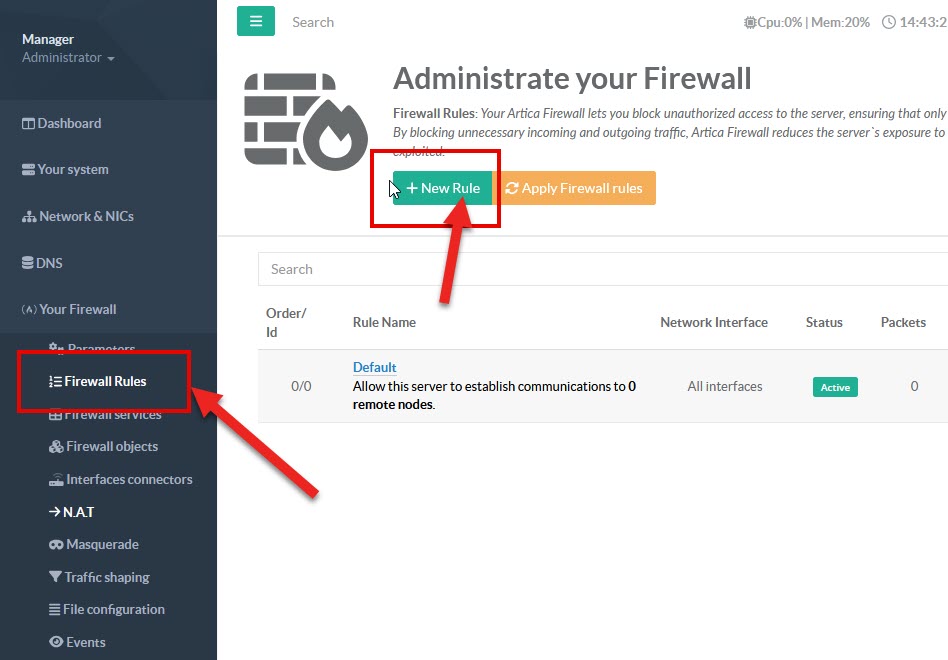
- On the left menu, go to “
Your Firewall” > “Firewall Rules” - Click on New Rule
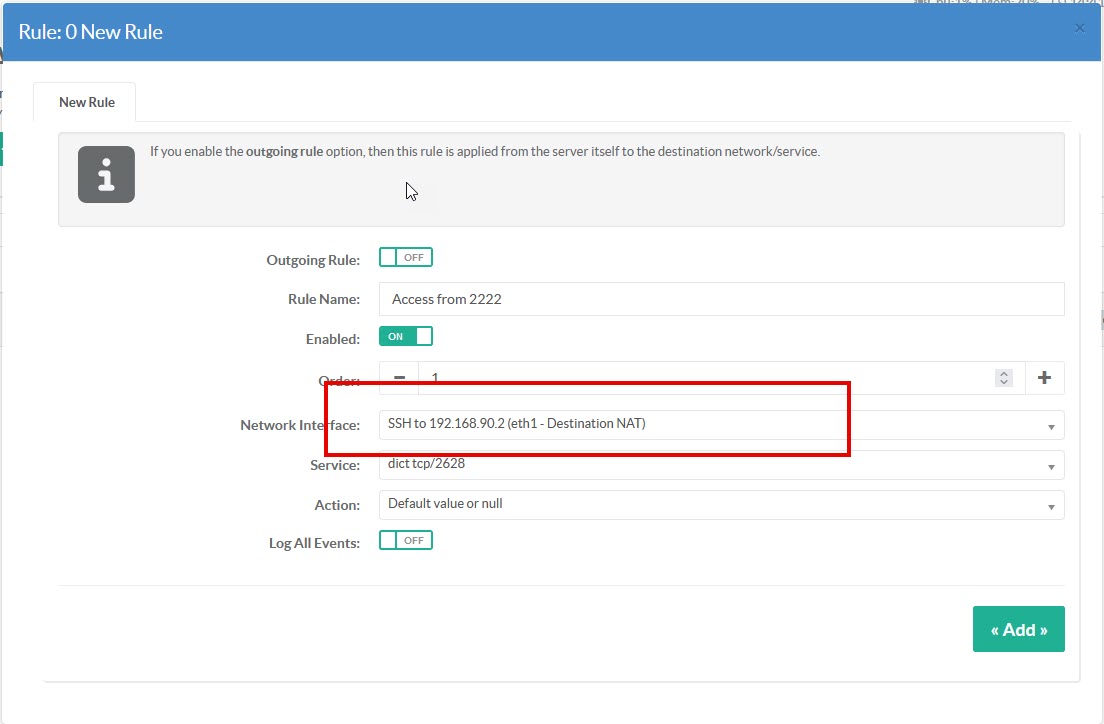
- Under rule, take a look at Network Interface.
- You'll see your NAT rules in the drop-down list.
- Fill in the rule using the NAT rule as the network interface.
Don't forget that you can use ACL objects to complete your rule