A DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) relay is an agent that forwards DHCP requests between different subnets to help hosts (clients) obtain an IP configuration from a DHCP server that might not be in the same subnet as the requesting host.
¶ Operating methods
Initial Request: When a client on a specific subnet boots up and wants to obtain an IP address, it sends out a DHCP request (typically in the form of a DHCPDISCOVER packet) that is broadcast to all DHCP servers.
- Relay Forwarding:
If the DHCP server is not in the same subnet as the client, the DHCP relay Service, which is usually set up on the router or switch of that subnet, detects this broadcast request.
It then takes this request and forwards it (usually as a unicast) to the designated DHCP server, but this time with the relay's IP address as the source address.
- Response from DHCP Server:
Once the DHCP server receives the request, it identifies the IP address of the relay and knows which subnet the original request came from.
It can then allocate an IP address from the appropriate address pool for that subnet and send back the IP configuration (typically in the form of aDHCPOFFERpacket) to the relay service. - Relay Back to Client:
The relay agent then forwards this offer back to the client.
Once the client accepts, the process continues until the client has a valid IP configuration.
The primary purpose of a DHCP relay is to allow DHCP clients to obtain IP configurations from a DHCP server that's not on their local subnet, without requiring a DHCP server on every subnet.
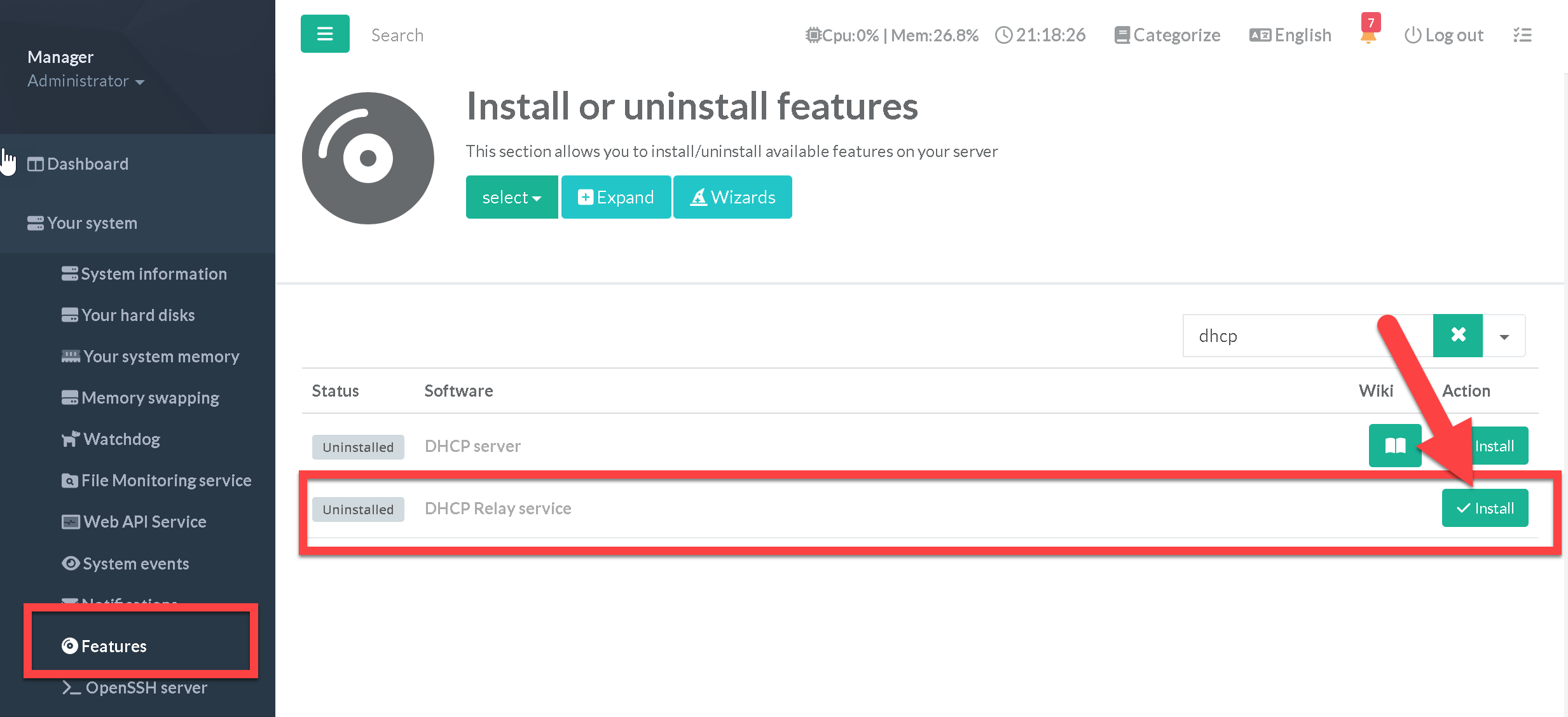
¶ Installing the DHCP relay service
- On the left menu, go to
Your System > Features - On the search field, type “dhcp”
- Click on Install button on the “DHCP relay service" row
¶ Configure the service
The DHCP Relay service configuration can be seen on the left menu on DHCP/TFTP > DHCP relay service
Initially, the service can't be started because you have to specify a mandatory parameters , these include DHCP backend servers
Click on the link to access to the configuration.
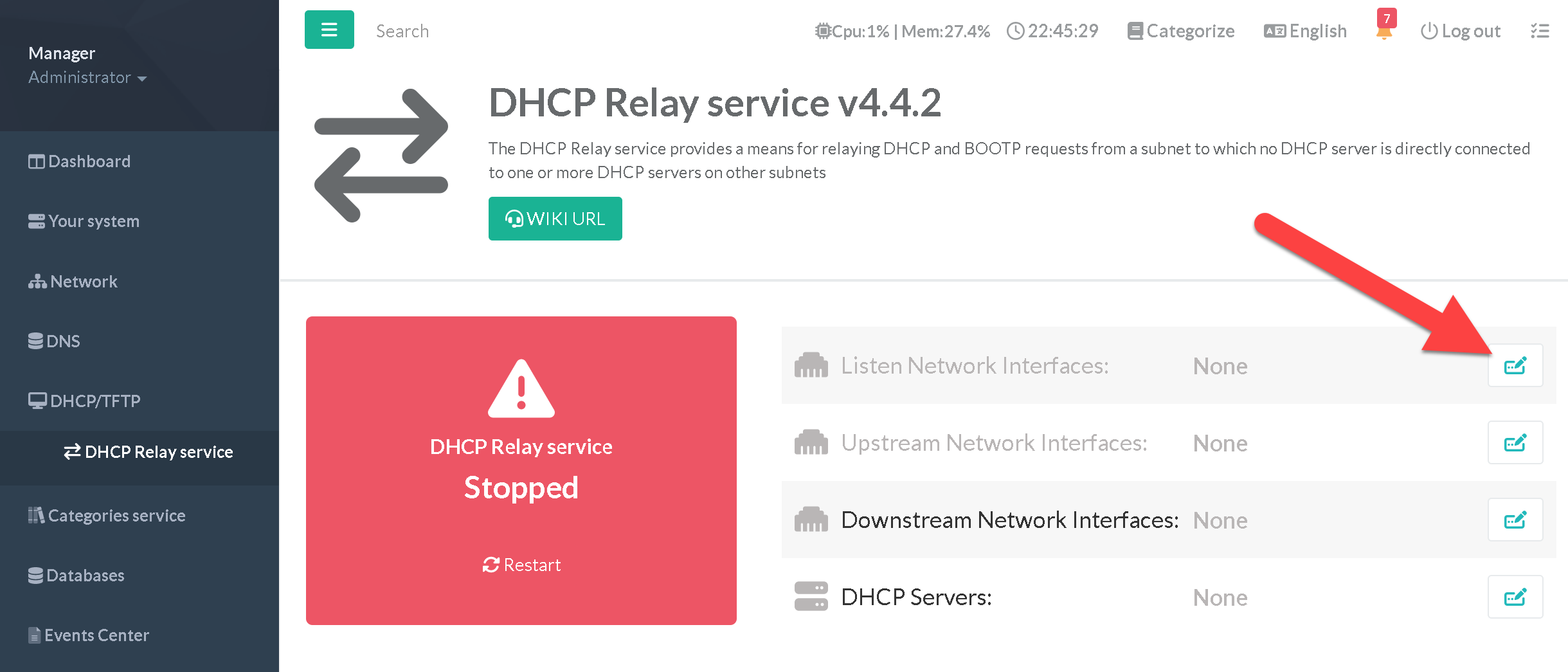
- Listen Network Interfaces:
Listen for DHCPv4/BOOTP traffic on interfaces (Multiple interfaces may be specified)
- Upstream network interfaces:
Interfaces from which replies from servers and other relay agents will be accepted (Multiple interfaces may be specified)
- Downstream network interfaces:
Interfaces from which requests from clients and other relay agents will be accepted (Multiple interfaces may be specified)
- DHCP servers:
A list of one or more server addresses must be specified on the command line, to which DHCP/BOOTP queries should be relayed.