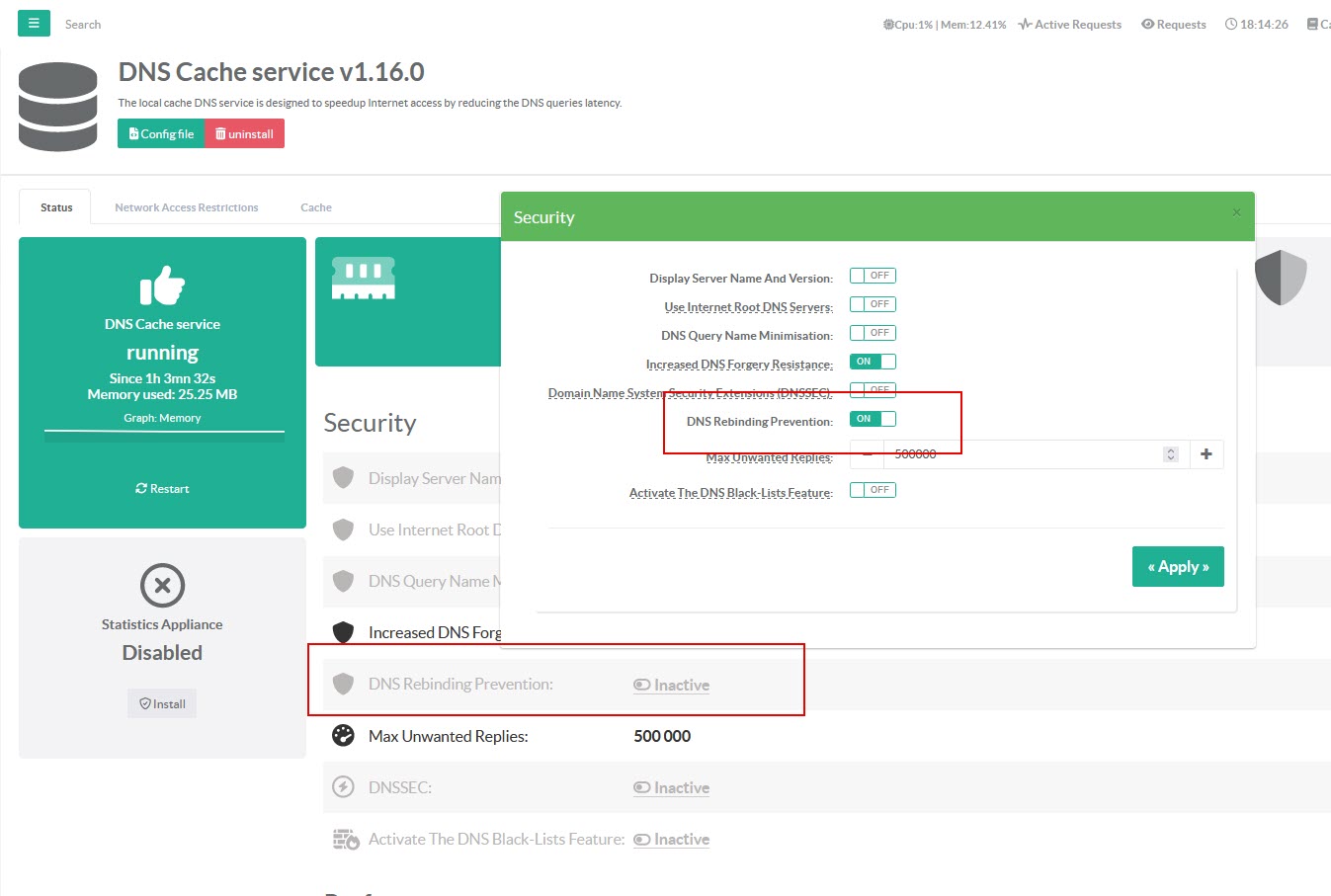
A DNS rebinding attack tricks a victim's browser into believing that an attacker-controlled domain points to a private (intranet) IP address. This can be used to circumvent the browser's same-origin policy and gain access to internal networks.
To prevent this kind of attack you can enable the “DNS Rebinding Prevention”
This option specifies 192.168.0.0/16, 169.254.0.0/16, 172.16.0.0/12, 10.0.0.0/8 ranges that are considered private and should not be forwarded to external DNS servers.
When a query result matches one of these addresses, the DNS service will not forward it to an upstream server, effectively blocking the DNS rebinding attempt.